2025 New 1Z0-051 Exam Dumps with PDF and VCE Free: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/1Z0-051/
We provide 1z0 051 pdf which are the best for clearing 1Z0-051 test, and to get certified by Oracle Oracle Database: SQL Fundamentals I. The 1z0 051 latest dumps free download pdf covers all the knowledge points of the real 1Z0-051 exam. Crack your Oracle 1Z0-051 Exam with latest dumps, guaranteed!
Free demo questions for Oracle 1Z0-051 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
Examine the structure and data in the PRICE_LIST table:
Name Null Type
PROD_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(3) PROD_PRICE VARCHAR2(10) PROD_ID PROD_PRICE
100 $234.55 101 $6,509.75 102 $1,234
You plan to give a discount of 25% on the product price and need to display the discount amount in the same format as the PROD_PRICE.
Which SQL statement would give the required result?
- A. SELECT TO_CHAR(prod_price* .25,'$99,999.99') FROM PRICE_LIST;
- B. SELECT TO_CHAR(TO_NUMBER(prod_price)* .25,'$99,999.00') FROM PRICE_LIST;
- C. SELECT TO_CHAR(TO_NUMBER(prod_price,'$99,999.99')* .25,'$99,999.00') FROM PRICE_LIST;
- D. SELECT TO_NUMBER(TO_NUMBER(prod_price,'$99,999.99')* .25,'$99,999.00') FROM PRICE_LIST;
Answer: B
Explanation: Use TO_NUMBER on the prod_price column to convert from char to number
to be able to multiply it with 0.25. Then use the TO_CHAR function (with
formatting'$99,999.00') to convert the number back to char.
Incorrect:
Not C: Use the formatting'$99,999.00' with the TO_CHAR function, not with the
TO_NUMBER function.
Note:
*
Using the TO_CHAR Function The TO_CHAR function returns an item of data type VARCHAR2. When applied to items of type NUMBER, several formatting options are available. The syntax is as follows: TO_CHAR(number1, [format], [nls_parameter]), The number1 parameter is mandatory and must be a value that either is or can be implicitly converted into a number. The optional format parameter may be used to specify numeric formatting information like width, currency symbol, the position of a decimal point, and group (or thousands) separators and must be enclosed in single
*
Syntax of Explicit Data Type Conversion Functions TO_NUMBER(char1, [format mask], [nls_parameters]) = num1 TO_CHAR(num1, [format mask], [nls_parameters]) = char1 TO_DATE(char1, [format mask], [nls_parameters]) = date1 TO_CHAR(date1, [format mask], [nls_parameters]) = char1
NEW QUESTION 2
View the Exhibit and examine the data in the PRODUCTS table. You need to display product names from the PRODUCTS table that belong to the 'Software/Other1 category with minimum prices as either $2000 or $4000 and no unit of measure. You issue thej following query: 
Which statement is true regarding the above query? 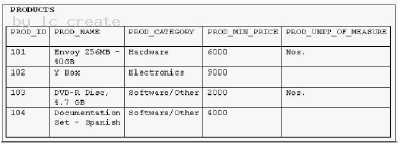
- A. It executes successfully but returns no resul
- B. It executes successfully and returns the required resul
- C. It generates an error because the condition specified for PROD_UNIT_OF_MEASURE is not vali
- D. It generates an error because the condition specified for the PROD_CATEGORY column is not vali
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 3
Where can sub queries be used? (Choose all that apply)
- A. field names in the SELECT statement
- B. the FROM clause in the SELECT statement
- C. the HAVING clause in the SELECT statement
- D. the GROUP BY clause in the SELECT statement
- E. the WHERE clause in only the SELECT statement
- F. the WHERE clause in SELECT as well as all DML statements
Answer: ABCF
Explanation:
SUBQUERIES can be used in the SELECT list and in the FROM, WHERE, and HAVING
clauses of a query.
A subquery can have any of the usual clauses for selection and projection. The following
are required clauses:
A SELECT list
A FROM clause
The following are optional clauses: WHERE GROUP BY HAVING
The subquery (or subqueries) within a statement must be executed before the parent query that calls it, in order that the results of the subquery can be passed to the parent.
NEW QUESTION 4
Examine the structure proposed for the TRANSACTIONS table: 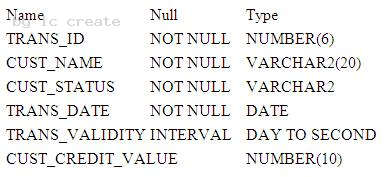
Which two statements are true regarding the storage of data in the above table structure? (Choose two.)
- A. The TRANS_DATE column would allow storage of dates only in the dd-mon-yyyy forma
- B. The CUST_CREDIT_VALUE column would allow storage of positive and negative integer
- C. The TRANS_VALIDITY column would allow storage of a time interval in days, hours, minutes, and second
- D. The CUST_STATUS column would allow storage of data up to the maximum VARCHAR2 size of 4,000 character
Answer: BD
Explanation:
B: The NUMBER datatype stores fixed and floating-point numbers. Numbers of virtually
any magnitude can be stored and are guaranteed portable among different systems
operating Oracle, up to 38 digits of precision.
The following numbers can be stored in a NUMBER column:
Positive numbers in the range 1 x 10-130 to 9.99...9 x 10125 with up to 38 significant digits Negative numbers from -1 x 10-130 to 9.99...99 x 10125 with up to 38 significant digits Zero Positive and negative infinity (generated only by importing from an Oracle Version 5 database)
D: The VARCHAR2 datatype stores variable-length character strings. When you create a table with a VARCHAR2 column, you specify a maximum string length (in bytes or characters) between 1 and 4000 bytes for the VARCHAR2 column. An interval literal specifies a period of time, and Oracle supports two types of interval literals: YEAR_TO_MONTH and DAY TO SECOND. For DAY TO SECOND, you can specify these differences in terms in terms of days, hours, minutes, and seconds. DAY TO SECOND contains a leading field and may contain an optional trailing field. If trailing field is specified it must be less significant than the leading field. For example, INTERVAL MINUTE TO DAY is not valid.
A DAY TO MINUTE interval considers an interval of days to the nearest minute. Reference: Oracle Database Concepts 10g, Native Datatypes
NEW QUESTION 5
View the Exhibit and examine the data in the PROJ_TASK_DETAILS table. 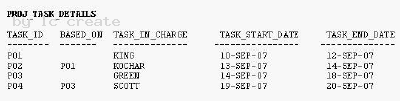
The PROJ_TASK_DETAILS table stores information about tasks involved in a project and the relation between them.
The BASED_ON column indicates dependencies between tasks. Some tasks do not depend on the completion of any other tasks.
You need to generate a report showing all task IDs, the corresponding task ID they are dependent on, and the name of the employee in charge of the task it depends on.
Which query would give the required result?
- A. SELECT p.task_id, p.based_on, d.task_in_charge FROM proj_task_details p JOIN proj_task_details d ON (p.based_on = d.task_id);
- B. SELECT p.task_id, p.based_on, d.task_in_charge FROM proj_task_details p LEFT OUTER JOIN proj_task_details d ON (p.based_on = d.task_id);
- C. SELECT p.task_id, p.based_on, d.task_in_charge FROM proj_task_details p FULL OUTER JOIN proj_task_details d ON (p.based_on = d.task_id);
- D. SELECT p.task_id, p.based_on, d.task_in_charge FROM proj_task_details p JOIN proj_task_details d ON (p.task_id = d.task_id);
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 6
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS table. 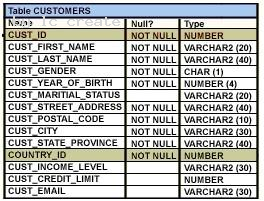
Which two tasks would require subqueries or joins to be executed in a single statement? (Choose two.)
- A. listing of customers who do not have a credit limit and were born before 1980
- B. finding the number of customers, in each city, whose marital status is 'married'
- C. finding the average credit limit of male customers residing in 'Tokyo' or 'Sydney'
- D. listing of those customers whose credit limit is the same as the credit limit of customers residing in the city 'Tokyo'
- E. finding the number of customers, in each city, whose credit limit is more than the average credit limit of all the customers
Answer: DE
Explanation:
Describe the Types of Problems That the Subqueries Can Solve There are many situations where you will need the result of one query as the input for another. Use of a Subquery Result Set for Comparison Purposes Which employees have a salary that is less than the average salary? This could be answered by two statements, or by a single statement with a subquery. The following example uses two statements: select avg(salary) from employees; select last_name from employees where salary < result_of_previous_query ;
Alternatively, this example uses one statement with a subquery:
select last_name from employees where salary < (select avg(salary)from employees);
In this example, the subquery is used to substitute a value into the WHERE clause of the
parent query: it is returning a single value, used for comparison with the rows retrieved by
the parent query.
The subquery could return a set of rows. For example, you could use the following to find
all departments that do actually have one or more employees assigned to them:
select department_name from departments where department_id in
(select distinct(department_id) from employees);
NEW QUESTION 7
See the Exhibit and examine the structure and data in the INVOICE table: Exhibit: 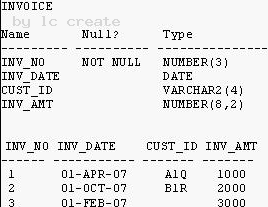
Which two SQL statements would execute successfully? (Choose two.)
- A. SELECT MAX(inv_date),MIN(cust_id) FROM invoice;
- B. SELECT AVG(inv_date-SYSDATE),AVG(inv_amt) FROM invoice;
- C. SELECT MAX(AVG(SYSDATE-inv_date)) FROM invoice;
- D. SELECT AVG(inv_date) FROM invoice;
Answer: AB
NEW QUESTION 8
Which statements are true regarding single row functions? (Choose all that apply.)
- A. MOD : returns the quotient of a division
- B. TRUNC : can be used with NUMBER and DATE values
- C. CONCAT : can be used to combine any number of values
- D. SYSDATE : returns the database server current date and time
- E. INSTR : can be used to find only the first occurrence of a character in a string
- F. TRIM : can be used to remove all the occurrences of a character from a string
Answer: BD
Explanation:
ROUND: Rounds value to a specified decimal TRUNC: Truncates value to a specified decimal MOD: Returns remainder of division SYSDATE is a date function that returns the current database server date and time.
Date-Manipulation Functions
Date functions operate on Oracle dates. All date functions return a value of the DATE data type except MONTHS_BETWEEN, which returns a numeric value. MONTHS_BETWEEN(date1, date2): Finds the number of months between date1 and date2. The result can be positive or negative. If date1 is later than date2, the result is positive; if date1 is earlier than date2, the result is negative. The noninteger part of the result represents a portion of the month. ADD_MONTHS(date, n): Adds n number of calendar months to date. The value of n must be an integer and can be negative. NEXT_DAY(date, 'char'): Finds the date of the next specified day of the week ('char') following date. The value of char may be a number representing a day or a character string. LAST_DAY(date): Finds the date of the last day of the month that contains date The above list is a subset of the available date functions. ROUND and TRUNC number functions can also be used to manipulate the date values as shown below: ROUND(date[,'fmt']): Returns date rounded to the unit that is specified by the format model fmt. If the format model fmt is omitted, date is rounded to the nearest day. TRUNC(date[, 'fmt']): Returns date with the time portion of the day truncated to the unit that is specified by the format model fmt. If the format model fmt is omitted, date is truncated to the nearest day.
The CONCAT Function
The CONCAT function joins two character literals, columns, or expressions to yield one larger character expression. Numeric and date literals are implicitly cast as characters when they occur as parameters to the CONCAT function. Numeric or date expressions are evaluated before being converted to strings ready to be concatenated. The CONCAT function takes two parameters. Its syntax is CONCAT(s1, s2), where s1 and s2 represent string literals, character column values, or expressions resulting in character values. The INSTR(source string, search item, [start position],[nth occurrence of search item]) function returns a number that represents the position in the source string, beginning from the given start position, where the nth occurrence of the search item begins: instr('http://www.domain.com','.',1,2) = 18 The TRIM function literally trims off leading or trailing (or both) character strings from a given source string:
NEW QUESTION 9
Which three statements/commands would cause a transaction to end? (Choose three.)
- A. COMMIT
- B. SELECT
- C. CREATE
- D. ROLLBACK
- E. SAVEPOINT
Answer: ACD
NEW QUESTION 10
Which statement is true regarding the default behavior of the ORDER BY clause?
- A. In a character sort, the values are case-sensitive
- B. NULL values are not considered at all by the sort operation
- C. Only those columns that are specified in the SELECT list can be used in the ORDER BY clause
- D. Numeric values are displayed from the maximum to the minimum value if they have decimal positions
Answer: A
Explanation:
Character Strings and Dates
Character strings and date values are enclosed with single quotation marks.
Character values are case-sensitive and date values are format-sensitive.
The default date display format is DD-MON-RR.
NEW QUESTION 11
The DBA issues this SQL command:
CREATE USER scott IDENTIFIED by tiger;
What privileges does the user Scott have at this point?
- A. no privileges
- B. only the SELECT privilege
- C. only the CONNECT privilege
- D. all the privileges of a default user
Answer: A
Explanation:
when a user is created, by default no privilege is granted
Incorrect Answer:
BSELECT is not grant
CCONNECT is not grant
Ddefault profile is grant by default not privilege.
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 13-6
NEW QUESTION 12
In which four clauses can a sub query be used? (Choose four.)
- A. in the INTO clause of an INSERT statement
- B. in the FROM clause of a SELECT statement
- C. in the GROUP BY clause of a SELECT statement
- D. in the WHERE clause of a SELECT statement
- E. in the SET clause of an UPDATE statement
- F. in the VALUES clause of an INSERT statement
Answer: ABDE
Explanation:
A: a sub query is valid on the INTO clause of an ISERT Statement
B: a sub query can be used in the FROM clause of a SELECT statement
D: a sub query can be used in the WHERE clause of a SELECT statement,
E: a sub query can be used in the SET clauses of an UPDATE statement,
Incorrect Answer:
Csub query cannot be used
F: is incorrect.
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 6-5
NEW QUESTION 13
You issue the following command to drop the PRODUCTS table:
SQL>DROP TABLE products;
What is the implication of this command? (Choose all that apply.)
- A. All data in the table are deleted but the table structure will remain
- B. All data along with the table structure is deleted
- C. All views and synonyms will remain but they are invalidated
- D. The pending transaction in the session is committed
- E. All indexes on the table will remain but they are invalidated
Answer: BCD
NEW QUESTION 14
See the Exhibit and Examine the structure of SALES and PROMOTIONS tables: Exhibit: 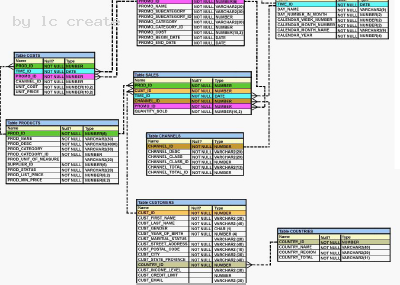
You want to delete rows from the SALES table, where the PROMO_NAME column in the PROMOTIONS table has either blowout sale or everyday low price as values.
Which DELETE statements are valid? (Choose all that apply.)
- A. DELETE FROM sales WHERE promo_id = (SELECT promo_id FROM promotions WHERE promo_name = 'blowout sale') AND promo_id = (SELECT promo_id FROM promotions WHERE promo_name = 'everyday low price');
- B. DELETE FROM sales WHERE promo_id = (SELECT promo_id FROM promotions WHERE promo_name = 'blowout sale') OR promo_id = (SELECT promo_id FROM promotions WHERE promo_name = 'everyday low price');
- C. DELETE FROM sales WHERE promo_id IN (SELECT promo_id FROM promotions WHERE promo_name = 'blowout sale' OR promo_name = 'everyday low price');
- D. D DELETE FROM sales WHERE promo_id IN (SELECT promo_id FROM promotions WHERE promo_name IN ('blowout sale','everyday low price'));
Answer: BCD
NEW QUESTION 15
Exhibit contains the structure of PRODUCTS table: 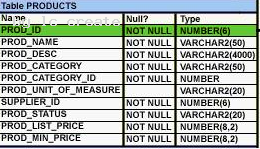
Evaluate the following query: 
What would be the outcome of executing the above SQL statement?
- A. It produces an error
- B. It shows the names of products whose list price is the second highest in the tabl
- C. It shown the names of all products whose list price is less than the maximum list price
- D. It shows the names of all products in the table
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 16
View the Exhibits and examine PRODUCTS and SALES tables. 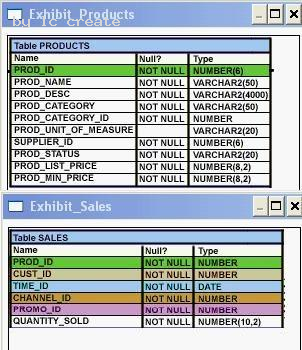
You issue the following query to display product name and the number of times the product has been sold:
SQL>SELECT p.prod_name, i.item_cnt FROM (SELECT prod_id, COUNT(*) item_cnt FROM sales GROUP BY prod_id) i RIGHT OUTER JOIN products p
ON i.prod_id = p.prod_id;
What happens when the above statement is executed?
- A. The statement executes successfully and produces the required outpu
- B. The statement produces an error because ITEM_CNT cannot be displayed in the outer quer
- C. The statement produces an error because a subquery in the FROM clause and outer-joins cannot be used togethe
- D. The statement produces an error because the GROUP BY clause cannot be used in a subquery in the FROM claus
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 17
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS and CUST_HISTORY tables. 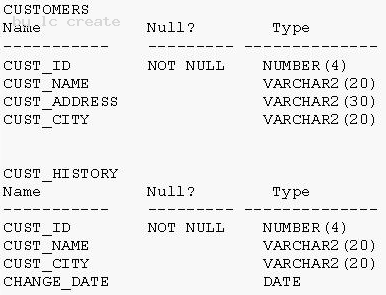
The CUSTOMERS table contains the current location of all currently active customers. The CUST_HISTORY table stores historical details relating to any changes in the location of all current as well as previous customers who are no longer active with the company.
You need to find those customers who have never changed their address.
Which SET operator would you use to get the required output?
- A. INTERSECT
- B. UNION ALL
- C. MINUS
- D. UNION
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 18
Examine the structure of the EMP_DEPT_VU view: 
Which SQL statement produces an error?
- A. SELECT * FROM emp_dept_vu;
- B. SELECT department_id, SUM(salary) FROM emp_dept_vu GROUP BY department_id;
- C. SELECT department_id, job_id, AVG(salary) FROM emp_dept_vu GROUP BY department_id, job_id;
- D. SELECT job_id, SUM(salary) FROM emp_dept_vu WHERE department_id IN (10,20) GROUP BY job_id HAVING SUM(salary) > 20000;
- E. None of the statements produce an error; all are vali
Answer: E
Explanation: Explanation: None of the statements produce an error. Incorrect Answer: AStatement will not cause error BStatement will not cause error CStatement will not cause error DStatement will not cause error
100% Valid and Newest Version 1Z0-051 Questions & Answers shared by Passcertsure, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.passcertsure.com/1Z0-051-test/ (New 292 Q&As)