2025 New 1Z0-051 Exam Dumps with PDF and VCE Free: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/1Z0-051/
Your success in 1z0 051 practice test is our sole target and we develop all our 1z0 051 pdf in a way that facilitates the attainment of this target. Not only is our 1z0 051 pdf material the best you can find, it is also the most detailed and the most updated. 1z0 051 dumps pdf for Oracle 1Z0-051 are written to the highest standards of technical accuracy.
Online 1Z0-051 free questions and answers of New Version:
NEW QUESTION 1
The STUDENT_GRADES table has these columns:
STUDENT_ID NUMBER(12)
SEMESTER_END DATE
GPA NUMBER(4,3)
Which statement finds the highest grade point average (GPA) per semester?
- A. SELECT MAX(gpa) FROM student_grades WHERE gpa IS NOT NULL;
- B. SELECT (gpa) FROM student_grades GROUP BY semester_end WHERE gpa IS NOT NULL;
- C. SELECT MAX(gpa) FROM student_grades WHERE gpa IS NOT NULL GROUP BY semester_end;
- D. SELECT MAX(gpa) GROUP BY semester_end WHERE gpa IS NOT NULL FROM student_grades;
- E. SELECT MAX(gpa) FROM student_grades GROUP BY semester_end WHERE gpa IS NOT NULL;
Answer: C
Explanation: Explanation: For highest gpa value MAX function is needed, for result with per semester GROUP BY clause is needed
Incorrect Answer: Aper semester condition is not included Bresult would not display the highest gpa value Dinvalid syntax error Einvalid syntax error Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 5-7
NEW QUESTION 2
The STUDENT_GRADES table has these columns:
STUDENT_IDNUMBER(12)
SEMESTER_ENDDATE
GPANUMBER(4,3)
The registrar has asked for a report on the average grade point average (GPA), sorted from the highest grade point average to each semester, starting from the earliest date.
Which statement accomplish this?
- A. SELECT student_id, semester_end, gpa FROM student_grades ORDER BY semester_end DESC, gpa DESC;
- B. SELECT student_id, semester_end, gpa FROM student_grades ORDER BY semester_end, gpa ASC
- C. SELECT student_id, semester_end, gpa FROM student_grades ORDER BY gpa DESC, semester_end ASC;
- D. SELECT student_id, semester_end, gpa FROM student_grades ORDER BY gpa DESC, semester_end DESC;
- E. SELECT student_id, semester_end, gpa FROM student_grades ORDER BY gpa DESC, semester_end ASC;
- F. SELECT student_id,semester_end,gpa FROM student_grades ORDER BY semester_end,gpa DESC
Answer: F
NEW QUESTION 3
In the CUSTOMERS table, the CUST_CITY column contains the value 'Paris' for the
CUST_FIRST_NAME 'ABIGAIL'.
Evaluate the following query: 
What would be the outcome?
- A. Abigail PA
- B. Abigail Pa
- C. Abigail IS
- D. an error message
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 4
See the Exhibit and examine the structure of the PROMOSTIONS table: Exhibit: 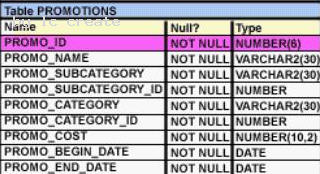
Which SQL statements are valid? (Choose all that apply.)
- A. SELECT promo_id, DECODE(NVL(promo_cost,0), promo_cost, promo_cost * 0.25, 100) "Discount" FROM promotions;
- B. SELECT promo_id, DECODE(promo_cost, 10000, DECODE(promo_category, 'G1', promo_cost *.25, NULL), NULL) "Catcost" FROM promotions;
- C. SELECT promo_id, DECODE(NULLIF(promo_cost, 10000), NULL, promo_cost*.25, 'N/A') "Catcost" FROM promotions;
- D. SELECT promo_id, DECODE(promo_cost, >10000, 'High', <10000, 'Low') "Range" FROM promotions;
Answer: AB
Explanation:
The DECODE Function Although its name sounds mysterious, this function is straightforward. The DECODE function implements ifthen-else conditional logic by testing its first two terms for equality and returns the third if they are equal and optionally returns another term if they are not. The DECODE function takes at least three mandatory parameters, but can take many more. The syntax of the function is DECODE(expr1,comp1, iftrue1, [comp2,iftrue2...[ compN,iftrueN]], [iffalse]).
NEW QUESTION 5
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the PROMOTIONS table. 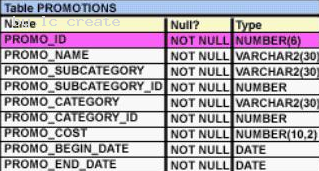
You have to generate a report that displays the promo name and start date for all promos that started after the last promo in the 'INTERNET' category.
Which query would give you the required output?
- A. SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_begin_date > ALL (SELECT MAX(promo_begin_date) FROM promotions )AND promo_category = 'INTERNET';
- B. SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_begin_date IN (SELECT promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_category='INTERNET');
- C. SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_begin_date > ALL (SELECT promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_category = 'INTERNET');
- D. SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_begin_date > ANY (SELECT promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_category = 'INTERNET');
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 6
Evaluate the following SQL statement:
Which statement is true regarding the outcome of the above query?
- A. It produces an error because the ORDER BY clause should appear only at the end of a compound query-that is, with the last SELECT statement
- B. It executes successfully and displays rows in the descending order of PROMO_CATEGORY
- C. It executes successfully but ignores the ORDER BY clause because it is not located at the end of the compound statement
- D. It produces an error because positional notation cannot be used in the ORDER BY clause with SET operators
Answer: A
Explanation:
Using the ORDER BY Clause in Set Operations
The ORDER BY clause can appear only once at the end of the compound query.
Component queries cannot have individual ORDER BY clauses.
The ORDER BY clause recognizes only the columns of the first SELECT query.
By default, the first column of the first SELECT query is used to sort the output in an
ascending order.
NEW QUESTION 7
Examine the structure of the TRANSACTIONS table:
Name Null Type
TRANS_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(3)
CUST_NAME VARCHAR2(30) TRANS_DATE DATE TRANS_AMT NUMBER(10,2)
You want to display the transaction date and specify whether it is a weekday or weekend. Evaluate the following two queries: 
Which statement is true regarding the above queries?
- A. Both give wrong result
- B. Both give the correct resul
- C. Only the first query gives the correct resul
- D. Only the second query gives the correct resul
Answer: C
Explanation:
Range Conditions Using the BETWEEN Operator Use the BETWEEN operator to display rows based on a range of values: SELECT last_name, salary FROM employees WHERE salary BETWEEN 2500 AND 3500; Range Conditions Using the BETWEEN Operator You can display rows based on a range of values using the BETWEEN operator. The range that you specify contains a lower limit and an upper limit. The SELECT statement in the slide returns rows from the EMPLOYEES table for any employee whose salary is between $2,500 and $3,500. Values that are specified with the BETWEEN operator are inclusive. However, you must specify the lower limit first. You can also use the BETWEEN operator on character values: SELECT last_name FROM employees WHERE last_name BETWEEN 'King' AND 'Smith';
NEW QUESTION 8
Top N analysis requires _____ and _____. (Choose two.)
- A. the use of rowid
- B. a GROUP BY clause
- C. an ORDER BY clause
- D. only an inline view
- E. an inline view and an outer query
Answer: CE
Explanation:
The correct statement for Top-N Analysis SELECT [coloumn_list], ROWNUM FROM (SELECT [coloumn_list]
FROM table
ORDER BY Top-N_coloumn)
WHERE ROWNUM <= N;
Incorrect Answer:
AROWID is not require
BGROUP BY clause is not require
DMust have inline view and outer query.
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 11-23
NEW QUESTION 9
You need to calculate the number of days from 1st January 2007 till date . Dates are stored in the default format of dd-mon-rr. Which two SQL statements would give the required output? (Choose two.)
- A. SELECT SYSDATE - '01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL:
- B. SELECT SYSDATE - TOJDATE(X)1/JANUARY/2007") FROM DUAL:
- C. SELECT SYSDATE - TOJDATE('01-JANUARY-2007') FROM DUAL:
- D. SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDAT
- E. 'DD-MON-YYYY') - '01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL:
- F. SELECT TO_DATE(SYSDAT
- G. *DD/MONTH/YYYY') - '01/JANUARY/2007' FROM DUAL:
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 10
A data manipulation language statement _____.
- A. completes a transaction on a table
- B. modifies the structure and data in a table
- C. modifies the data but not the structure of a table
- D. modifies the structure but not the data of a table
Answer: C
Explanation:
modifies the data but not the structure of a table
Incorrect Answer:
ADML does not complete a transaction
BDDL modifies the structure and data in the table
DDML does not modified table structure.
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 8-3
NEW QUESTION 11
View the Exhibit and examine the data in the PROMOTIONS table.
PROMO_BEGIN_DATE is stored in the default date format, dd-mon-rr.
You need to produce a report that provides the name, cost, and start date of all promos in the POST category that were launched before January 1, 2000.
Which SQL statement would you use?
- A. SELECT promo_name, promo_cost, promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_category = 'post' AND promo_begin_date < '01-01-00';
- B. SELECT promo_name, promo_cost, promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_cost LIKE 'post%' AND promo_begin_date < '01-01-2000';
- C. SELECT promo_name, promo_cost, promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_category LIKE 'P%' AND promo_begin_date < '1-JANUARY-00';
- D. SELECT promo_name, promo_cost, promo_begin_date FROM promotions WHERE promo_category LIKE '%post%' AND promo_begin_date < '1-JAN-00';
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 12
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the PROMOTIONS, SALES, and CUSTOMER tables. 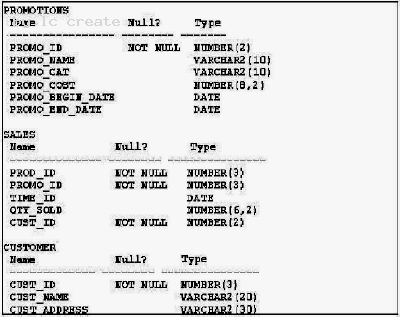
You need to generate a report showing the promo name along with the customer name for all products that were sold during their promo campaign and before 30th October 2007.
You issue the following query:
Which statement is true regarding the above query?
- A. It executes successfully and gives the required resul
- B. It executes successfully but does not give the required resul
- C. It produces an error because the join order of the tables is incorrec
- D. It produces an error because equijoin and nonequijoin conditions cannot be used in the same SELECT statemen
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 13
A SELECT statement can be used to perform these three functions:
Choose rows from a table.
Choose columns from a table
Bring together data that is stored in different tables by creating a link between
them.
Which set of keywords describes these capabilities?
- A. difference, projection, join
- B. selection, projection, join
- C. selection, intersection, join
- D. intersection, projection, join
- E. difference, projection, product
Answer: B
Explanation: Explanation: choose rows from a table is SELECTION,
Choose column from a table is PROJECTION
Bring together data in different table by creating a link between them is JOIN.
Incorrect Answer:
Aanswer should have SELECTION, PROJECTION and JOIN.
Canswer should have SELECTION, PROJECTION and JOIN.
Danswer should have SELECTION, PROJECTION and JOIN.
Eanswer should have SELECTION, PROJECTION and JOIN.
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 1-6
NEW QUESTION 14
SLS is a private synonym for the SH.SALES table.
The user SH issues the following command:
DROP SYNONYM sls;
Which statement is true regarding the above SQL statement?
- A. Only the synonym would be droppe
- B. The synonym would be dropped and the corresponding table would become invali
- C. The synonym would be dropped and the packages referring to the synonym would be droppe
- D. The synonym would be dropped and any PUBLIC synonym with the same name becomes invali
Answer: A
Explanation:
A synonym is an alias for a table (or a view). Users can execute SQL statements against the synonym, and the database will map them into statements against the object to which the synonym points.
Private synonyms are schema objects. Either they must be in your own schema, or they must be qualified with the schema name. Public synonyms exist independently of a schema. A public synonym can be referred to by any user to whom permission has been granted to see it without the need to qualify it with a schema name.
Private synonyms must be a unique name within their schema. Public synonyms can have the same name as schema objects. When executing statements that address objects without a schema qualifier, Oracle will first look for the object in the local schema, and only if it cannot be found will it look for a public synonym.
NEW QUESTION 15
You are currently located in Singapore and have connected to a remote database in
Chicago.
You issue the following command:
Exhibit: 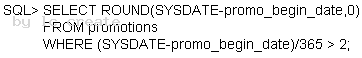
PROMOTIONS is the public synonym for the public database link for the PROMOTIONS table.
What is the outcome?
- A. Number of days since the promo started based on the current Singapore data and tim
- B. An error because the ROUND function specified is invalid
- C. An error because the WHERE condition specified is invalid
- D. Number of days since the promo started based on the current Chicago data and time
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 16
You need to create a table for a banking application. One of the columns in the table has the following requirements:
You want a column in the table to store the duration of the credit period
The data in the column should be stored in a format such that it can be easily added and subtracted with DATE data type without using conversion
The maximum period of the credit provision in the application is 30 days
the interest has to be calculated for the number of days an individual has taken a credit for
Which data type would you use for such a column in the table?
- A. INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH
- B. NUMBER
- C. TIMESTAMP
- D. DATE
- E. INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND
Answer: E
NEW QUESTION 17
Examine the data in the LIST_PRICE and MIN_PRICE columns of the PRODUCTS table: 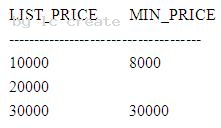
Which two expressions give the same output? (Choose two.)
- A. NVL(NULLIF(list_price, min_price), 0)
- B. NVL(COALESCE(list_price, min_price), 0)
- C. NVL2(COALESCE(list_price, min_price), min_price, 0)
- D. COALESCE(NVL2(list_price, list_price, min_price), 0)
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Using the COALESCE Function
.
The advantage of the COALESCE function over the NVL function is that the COALESCE
function can take multiple alternate values.
.
If the first expression is not null, the COALESCE function returns that expression;
otherwise, it does a COALESCE of the remaining expressions.
Using the COALESCE Function
The COALESCE function returns the first non-null expression in the list.
Syntax
COALESCE (expr1, expr2, ... exprn) In the syntax:
.
expr1 returns this expression if it is not null
.
expr2 returns this expression if the first expression is null and this expression is not null
.
exprn returns this expression if the preceding expressions are null Note that all expressions must be of the same data type.
NEW QUESTION 18
Which CREATE TABLE statement is valid?
- A. CREATE TABLE ord_details (ord_no NUMBER(2) PRIMARY KEY, item_no NUMBER(3) PRIMARY KEY, ord_date DATE NOT NULL);
- B. CREATE TABLE ord_details (ord_no NUMBER(2) UNIQUE, NOT NULL, item_no NUMBER(3), ord_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE NOT NULL);
- C. CREATE TABLE ord_details (ord_no NUMBER(2) , item_no NUMBER(3), ord_date DATE DEFAULT NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT ord_uq UNIQUE (ord_no), CONSTRAINT ord_pk PRIMARY KEY (ord_no));
- D. CREATE TABLE ord_details (ord_no NUMBER(2), item_no NUMBER(3), ord_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT ord_pk PRIMARY KEY (ord_no, item_no));
Answer: D
Explanation:
PRIMARY KEY Constraint
A PRIMARY KEY constraint creates a primary key for the table. Only one primary key can be created for each table. The PRIMARY KEY constraint is a column or a set of columns that uniquely identifies each row in a table. This constraint enforces the uniqueness of the column or column combination and ensures that no column that is part of the primary key can contain a null value. Note: Because uniqueness is part of the primary key constraint definition, the Oracle server enforces the uniqueness by implicitly creating a unique index on the primary key column or columns.
P.S. Easily pass 1Z0-051 Exam with 292 Q&As prep-labs.com Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest prep-labs.com 1Z0-051 Dumps: https://www.prep-labs.com/dumps/1Z0-051/ (292 New Questions)